Furnace Ignitor Lights but No Flame (Fixed)

When a furnace ignitor lights up but there’s no flame, it can be a frustrating experience.
This guide provides detailed solutions to help identify and fix the root causes efficiently.
A furnace that fails to ignite fully can leave your home without heat during crucial times. Below, we dive into every aspect of why this happens and how you can get your furnace back up and running.
Understanding How a Furnace Ignition System Works
How Does the Ignition System Operate?
In modern furnaces, the ignitor’s job is to heat up and ignite the gas, producing a flame to start the heating cycle. This process typically follows these steps:
- Thermostat Request: The thermostat signals the furnace to ignite.
- Ignitor Activation: The ignitor glows to a high temperature.
- Gas Valve Opens: Gas flows toward the ignitor.
- Flame Sensor Checks Ignition: The flame sensor confirms a flame.
- Heating Cycle Continues: If all goes well, the system continues heating.
Possible Causes and Solutions When Furnace Ignitor Lights but No Flame

1. Faulty Gas Valve
The gas valve controls the flow of fuel into the furnace. When it malfunctions, the ignitor may light, but without gas flow, there will be no flame.
- Solution: Check if the gas valve is open and receiving power. If it’s open but still unresponsive, it may need replacement. A certified technician should handle this due to gas safety concerns.
2. Dirty Flame Sensor
The flame sensor detects if a flame is present and automatically shuts down the furnace if it doesn’t. When dirty, it may fail to detect the flame, causing the furnace to stop.
- Solution: Clean the flame sensor with fine-grit sandpaper or an emery cloth. Reinstall the sensor and try to ignite the furnace again.
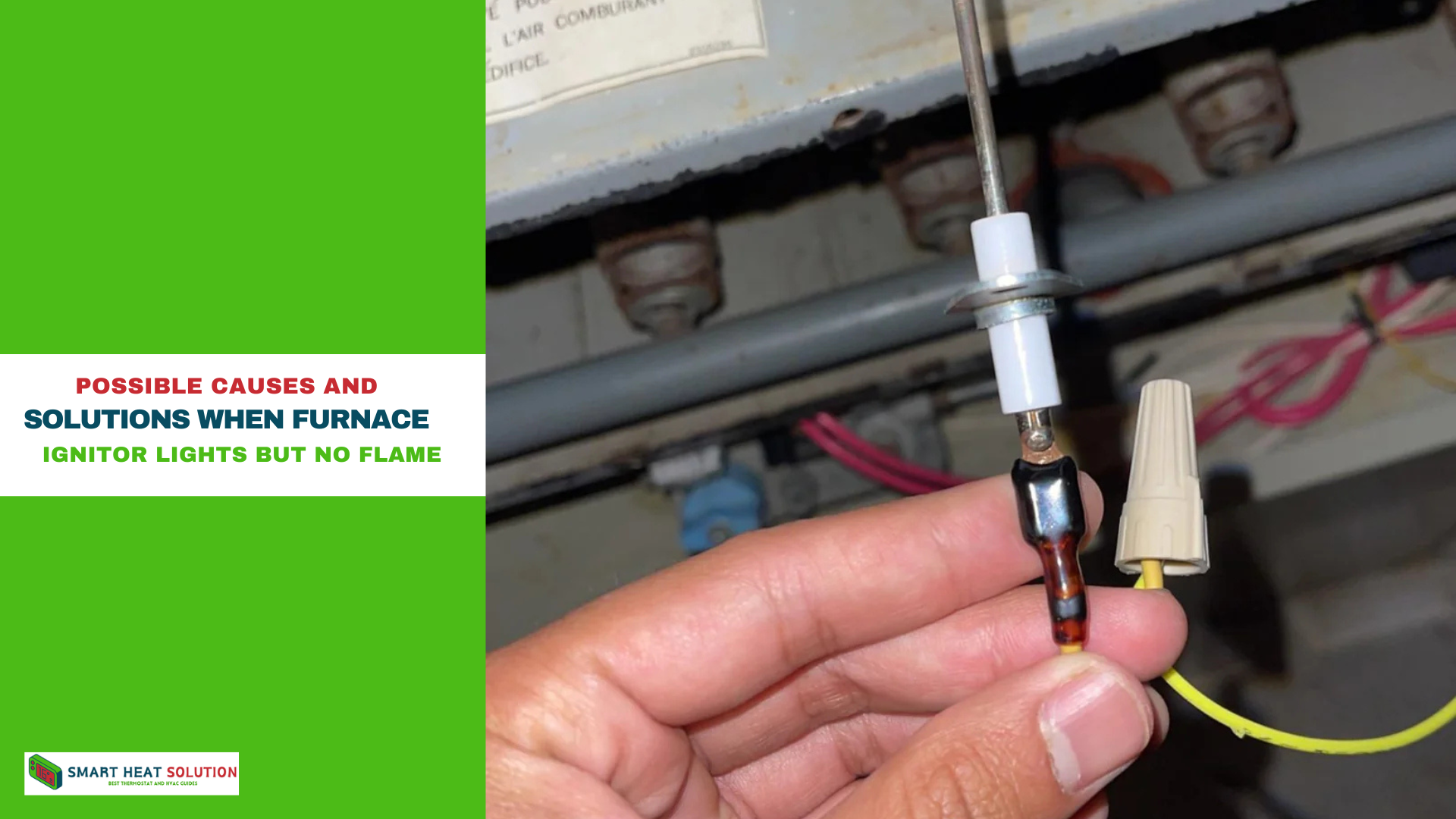
3. Ignitor Malfunction
If the ignitor is damaged, it may glow but not reach the temperature required to ignite the gas. This is common in ignitors that are old or brittle.
- Solution: Inspect the ignitor for visible cracks or wear. If damaged, replace the ignitor. For compatibility, ensure the replacement ignitor matches the furnace model.
4. Gas Pressure Issues
Low gas pressure can cause the ignitor to glow without producing a stable flame. Low gas pressure could result from a faulty regulator or issues in the gas line.
- Solution: A professional can measure gas pressure and, if necessary, adjust or repair the gas line components.
5. Clogged Furnace Burner
A clogged burner prevents gas from flowing properly, which can lead to the ignitor glowing but no flame igniting. Dust and debris are common culprits in clogging burners.
- Solution: Turn off power to the furnace and use compressed air to clear debris from the burners. If unsure about disassembly, consult a professional technician.
How to Test and Replace Key Components
Testing the Ignitor
To determine if the ignitor is the issue, test for continuity using a multimeter:
- Step 1: Disconnect the furnace power.
- Step 2: Locate the ignitor and disconnect its wiring.
- Step 3: Set the multimeter to the continuity setting and check across the ignitor’s terminals.
If there’s no continuity, the ignitor is faulty and needs replacement.
Inspecting the Gas Valve and Flame Sensor
- Gas Valve: Confirm it opens by listening for a “click” sound after the ignitor activates.
- Flame Sensor: If the flame ignites but then shuts down quickly, clean or replace the flame sensor.
Additional Issues That Can Cause Ignition Failure
Furnace Lockout Mode
Many furnaces enter a lockout mode after repeated ignition failures as a safety measure. When in lockout mode, the furnace temporarily disables further ignition attempts.
- Solution: Check the furnace manual for lockout reset instructions. Most systems can be reset by switching the power off for a few minutes.
Blocked Air Intake or Exhaust
If the air intake or exhaust is blocked, it may prevent proper combustion, resulting in ignition issues.
- Solution: Clear any debris from the intake or exhaust vents. Ensure no obstructions are preventing airflow to the furnace.
FAQs on Furnace Ignition Issues
Why does my furnace ignitor glow but not ignite?
Several factors can cause this, including a faulty gas valve, low gas pressure, or a dirty flame sensor. Refer to each component’s troubleshooting steps to isolate the cause.
How often should I clean the flame sensor?
To ensure consistent operation, clean the flame sensor once a year or whenever the furnace shows ignition issues.
Can I repair the ignitor myself?
You can replace the ignitor if you’re comfortable handling electrical components. Ensure the furnace is disconnected from power, and follow the furnace manual.
What should I do if the furnace keeps going into lockout mode?
Continuous lockout mode may indicate deeper system issues. Contact a professional technician to prevent potential damage and ensure safety.
Final Thoughts on Resolving Ignitor and Flame Issues
If your furnace ignitor lights but no flame appears, one or more components in the ignition system are likely failing. By following this guide, you can troubleshoot common causes and find solutions that restore your furnace’s function. Regular maintenance of critical parts, such as cleaning the flame sensor and inspecting the ignitor, can also help prevent future ignition issues.
For persistent problems, a qualified HVAC technician can perform a thorough assessment, ensuring your furnace runs efficiently and safely during cold seasons.

I’m Alan William’s, the founder of SmartHeatSolution.com. I am from California, USA, I’m passionate about innovative heating technologies and their impact on our homes and businesses. With a background in electrican and home repair , I aim to make smart, energy-efficient heating accessible to everyone. When I’m not writing, I’m likely interested in all the thermostat brands and their new technnology. Thanks for stopping by!